Table of Contents
What is WordPress?
WordPress is a software or a website builder developed in 2003 that manages the content of your website; you can manage all the content of your website by using WordPress. Such as, posting blogs, creating webpages, etc. There are several website builders on the market you can explore to gain knowledge (Drupal, Joomla, etc), but WordPress is the most prominent and user-friendly website builder in terms of Cost and SEO factors for bloggers to work with. And WordPress is free, diverse, and flexible for making all kinds of websites without needing any code to build a website from scratch, such as personal blogs to eCommerce websites. Almost 35% of all websites on the internet use WordPress.
Types of WordPress:
There are two types of WordPress:
1. A self-hosted WordPress website called WordPress.org means you choose a hosting plan for your website from a third-party hosting provider according to your needs and research. And it is free to download and customize your website with full control by accessing themes and plugins, you only need to buy a hosting and a domain name for your website to start. It is affordable and great for monetization & customization.
2. Hosted WordPress website named WordPress.com which is mainly a hosting service from WordPress company like other third party hosting companies. Although they offer a free plan to start, the name WordPress will be attached to your domain name, such as www.yourdomain.wordpress.com. And WordPress.com comes with limitations like limited storage, plugins, and themes, running their ads on your website, etc.
Installing WordPress on your website:
At first, you might get perplexed to download and install WordPress on your website due to the process of going to WordPress.org and then downloading the file, etc. But the hosting companies make it easy for you by their step by step processing from buying a domain to setting up your wordpress website. For example, Hostinger uses their WordPress auto-installer tool to install WordPress with ease.
* Lets install wordpress through hostinger: Hostinger is a hosting provider, popular for web-hosting. And they offer three web-hosting plans to get started:
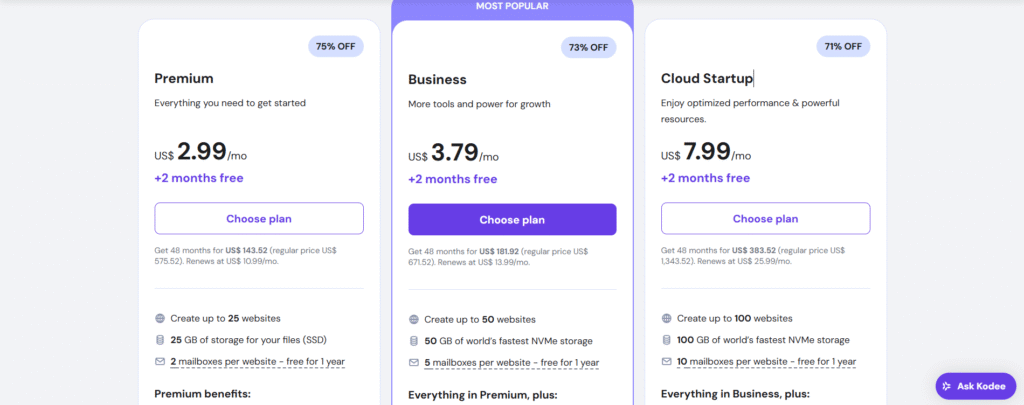
I like their pricing because they are so affordable and suitable for the start up business and of course as your website grows you can change and upgrade your plan anytime. They offer three plans: Premium, Business, and Cloud startup. You need to choose any of these plans based on your website’s needs. Furthermore, each plans come with different benefits:
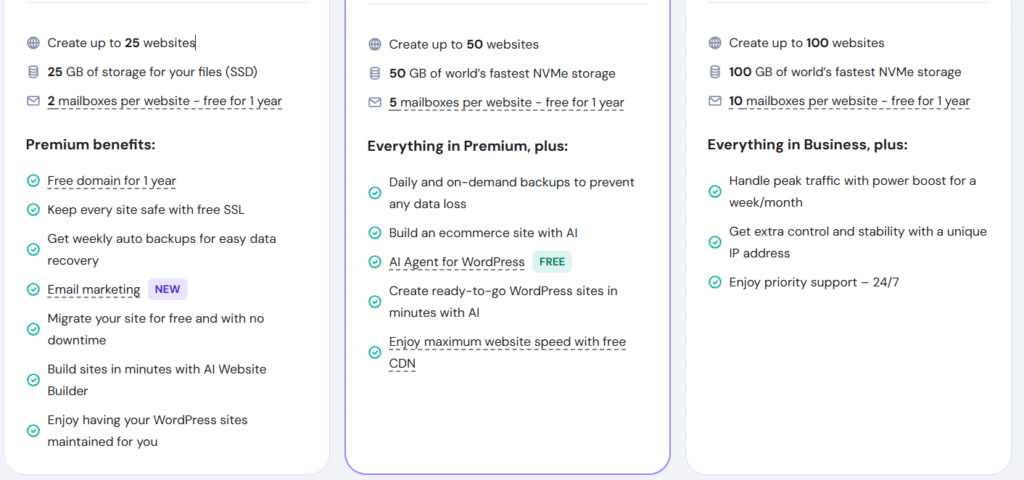
I would recommend selecting the Premium plan to get started as a beginner. You can create up to 25 websites with 25 GB SSD storage which is more than enough for anyone who wants to start their online presence. Additionally, you don’t need to pay for your domain for the first year which is priced $9.99 and 1 year free email marketing to your subscribers. And all of these services you’ll get cheaply. Follow the instruction below:
Choose the Premium plan, then you’ll see this interface:
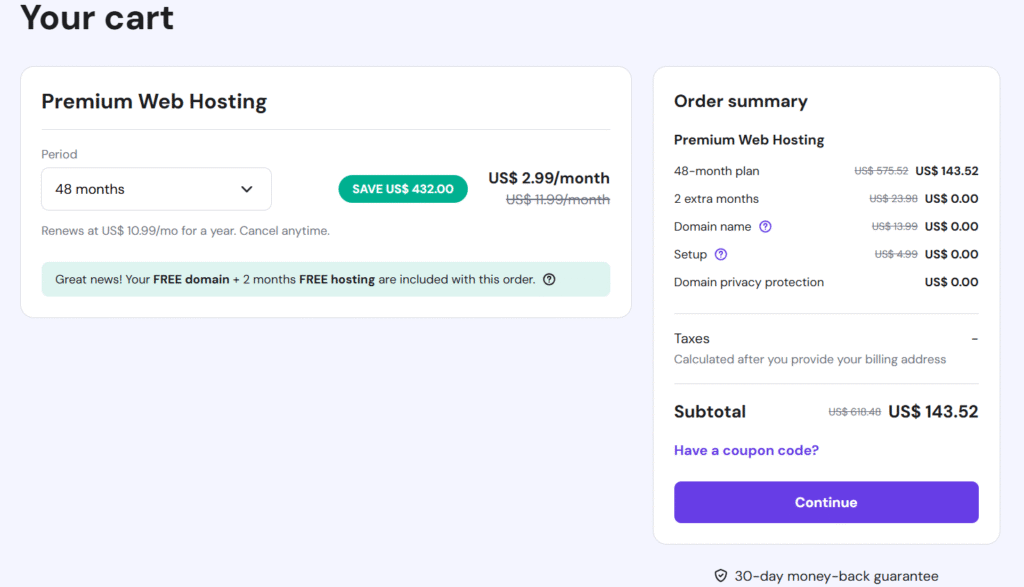
They have four period options, (1 month, 12 months, 24 months, and 48 months). I suggest you choose the 12 month or 48 month plan. Plus, apply coupon code to get a 10% discount. The 1 year option will cost totally $43.09 and for the 48 months option total cost will be $129.07. So, decide one of these, then click continue button and fill the billing address form:
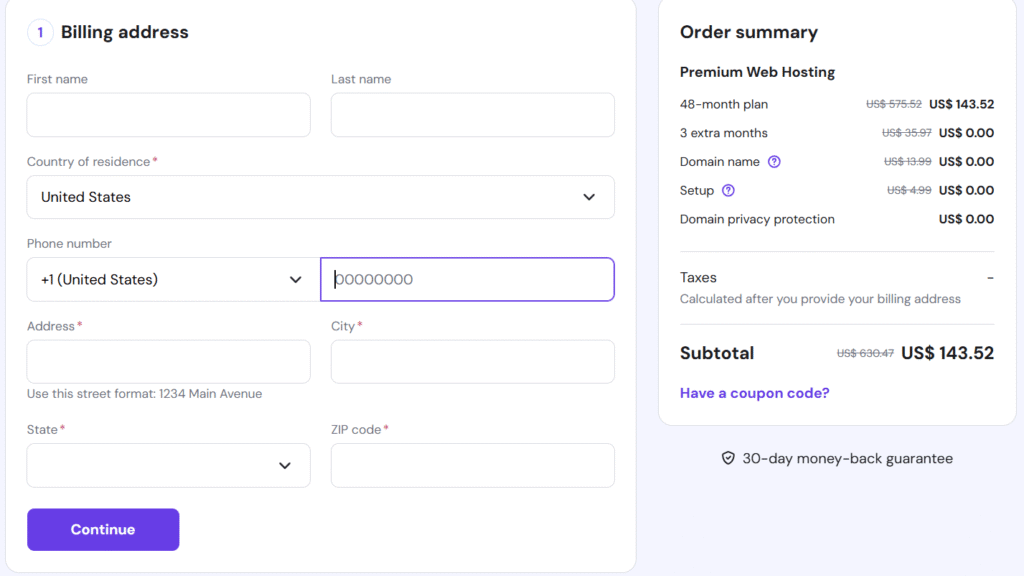
Next, choose the payment option you want and pay for your web hosting: remember that payment options will be extended based on your selected country if the Hostinger includes.
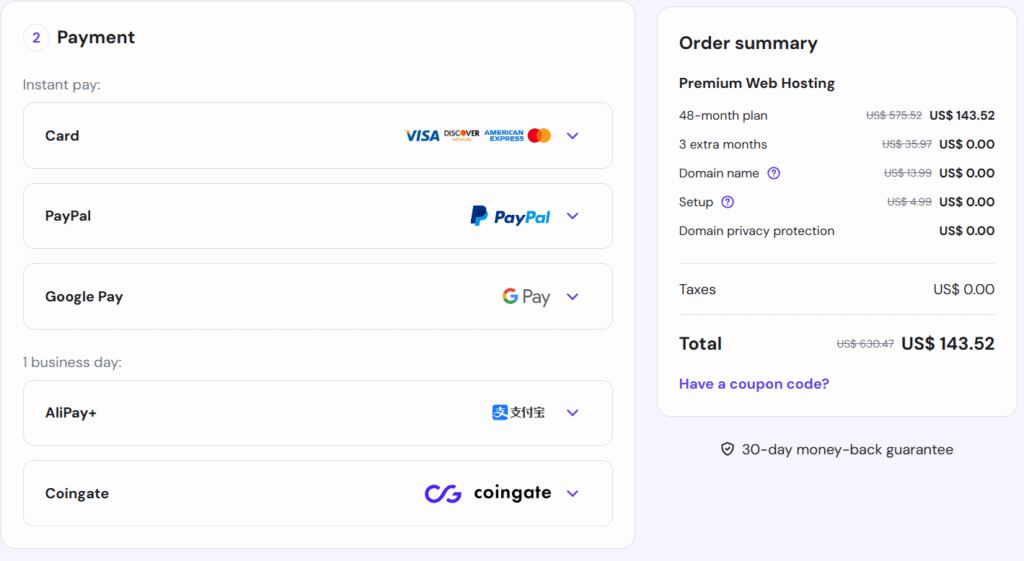
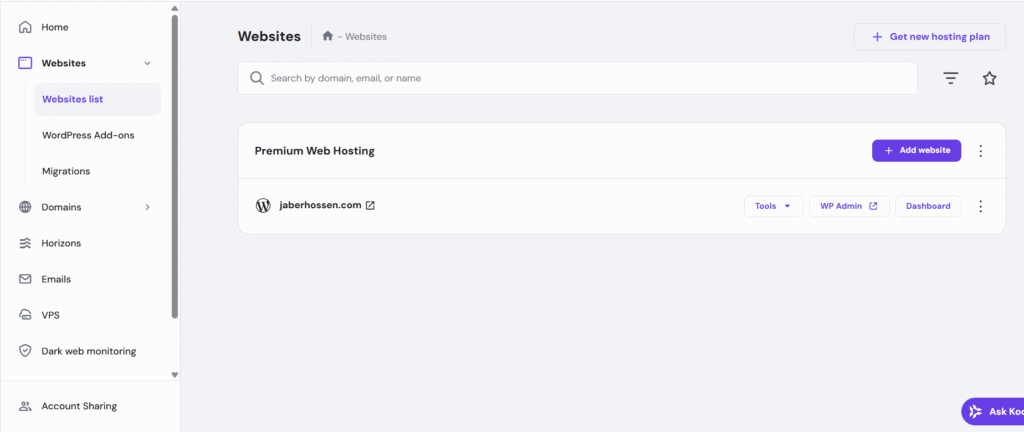
*** After submitting the payment, it will take you to the hostinger’s dashboard where you have to select and add a new website to your account, then choose the WordPress platform for your website.
- Enter your email address and strong password. And write down it anywhere because it will need to log into your wordpress account later.
- Then, they will offer to install plugins and themes. Skip them because you can download them later.
- Choose a DNS server region based on your target audience due to speed and quick upload time of your website.
- Then, Hostinger’s Auto-installer will install WordPress automatically and direct you to the WordPress dashboard or you can explore the Hostinger’s hpanel/ control panel.
Learn WordPress point by point:
After installing WordPress, we’ll have the WP Dashboard to do everything from customization to uploading content, and so on.
Dashboard: Dashboard shows an overview of your full website. It reveals an interface where you can see everything at once and can navigate them quickly and easily which is called the home section. And also an update section where all the required updates of plugins, & themes, will be shown to you so that you can update them at once.
Post: Post is the primary content of your website, like a blog or article. This blog, right now you’re reading, is also a post, or see below:
And under the post section, it has four subsections:
- All posts: here you can see all the posts you’ve uploaded.
- Add post: add post used for creating a new blog or content for your website.
- Categories: Categories are the stacks of your store. Each stack is named differently such as clothing, accessories, etc. Similarly, in a website categories used for organizing your posts like learn a language, learn digital literacy, book notes, lifestyle and under each category contains all the relevant posts. Categorizing is vital for smooth navigation and reader engagement.
- Tags: Tags are slightly different from categories, category grouping your posts orderly. Tags are types of keywords that are used for finding relevant posts across a website. Tags are great for user experience and google seo ranking.
Media: The media section is like the Technical room of an institution. Likewise, all the images, videos, audios, and documents of a website are stored in the media section to use across a website posts, pages, etc. It has two suboptions:
- Media Library: Every media file is stored in this section.
- Add Media file: it is used for adding images, videos, and audios to the media library for later use in posts, customizing page sections, etc.
Pages: Pages are the rooms of a building and each room has its unique decoration and specific intentional use. Such as, a dining room decorated with a sofa, dining table, etc, intended to invite guests, family gathering, and celebrating special events, unlike the bedroom and kitchen room. Exactly, a website has pages based on intentions or purpose like home page, about me page, blog page, resources page, etc. However, a website can have a subpage called child page which is part of a parent page. For example, inside of a resources page, you can have subpages of courses, blogs, events, etc.
- All pages: All pages section showcases all published and private pages of a website at once.
- Add page: add page is used for creating and designing a new page for a website by clicking add page in WordPress.
Comments: in the comments section, all the comments across a website from posts to pages are allocated at once to manage. You can see comments like pending, approved, spam, and trash.
Appearance: Appearance is a functional and visible look of a website. It is the engineering and designing of your pages and website, like rooms and buildings. And WordPress integrates with themes to do it.
- Theme: Theme is a type of file that is used for enhancing visual appearance to a website visitor to navigate effortlessly. Without a theme your website will resemble a dry tree. The theme gives a life to a website by styling and functioning appropriately like covering the dry tree with leaves and fruits. Generally, you can use wordpress built-in default themes or download authoritative third-party themes by clicking the add theme option on the left corner. Remember, theme doesn’t bother a website posts and pages, it just styles the outfit or dress of a website that means you can change theme anytime.
- Editor: Editor is enabled when you access a theme. When you download your chosen theme and activate it, then it will have a customization option to design your website by navigating it.
Plugins: Plugin is a software or app that collaborates with your WordPress to extend functionalities. And I call it “Plug in” which means plugging a software into a WordPress to add new features to a website, like a charger into an electric plug. Exactly, consider a WordPress plugin option, which is plug and a charger pin connected to the software. There are many types of plugins, like security plugins, e-Commerce, seo plugins.
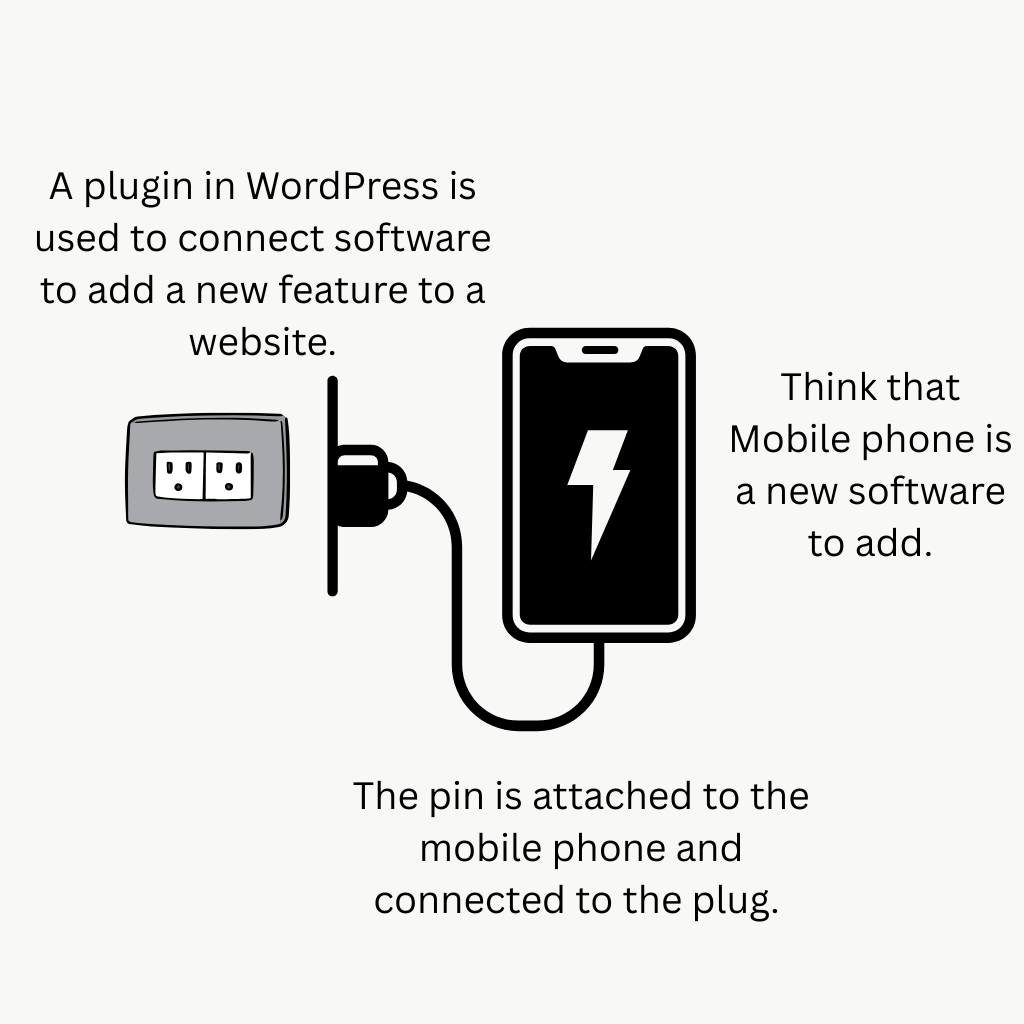
- Installed Plugins: You can see your downloaded activated or deactivated plugins at glance and can delete as well.
- Add plugin: To add plugin you have to click to this option, then explore thousands plugins and download any of these that require.
Users: Users option in a WordPress website refers to users who can access a wordpress dashboard. Remember, visitors of a website are not considered as users because they can only access your wordpress website, not the Dashboard.
- All Users: You can see all types of your wordpress users at once.
- Add Users: This option is used for adding new users to your wordpress dashboard. Generally, there are five types of users role in wordpress:
- Administrator role: Administrator role means someone owner of a wordpress website who has full control, he can do anything he wants from installing plugins, themes to deleting contents or adding and removing new users. In other words, he is omniscient of a wordpress website.
- Editor Role: Editor of a wordpress website only has full control on the post & comment section, he can publish and delete posts and comments of him or others. Plus, they can add media files to their contents.
- Author Role: Authors have more narrower control than editors, only can handle their own posts. They can only publish and delete their posts, not others. Remember, they don’t have control on the comments section, but they can upload media files for their posts.
- Contributor Role: Contributor can write or edit posts, but can not access to publishing them. They have to rely on a revision process where someone from users who has control on publishing and editing, will review the post and publish or delete it.
- Subscriber Role: Subscribers have no control on any kinds of items of your WordPress admin or dashboard area. They are the sole subscriber to your website contents, email, or buyer. It is used for accessing and selling the exclusive contents to audiences
- Additional: You can manage and handle different user roles through plugin liker members. For more secure management, there are several quality plugins to assist you.
- Profile: When you buy a domain and hosting and install wordpress through Hostinger, you’ll automatically have administrator user role based on your password and email you’ve given. Now, in this profile section, you can change your password, email, add profile picture, change language, customize the color scheme of your admin area, etc.
Tools: Tools are mechanical equipment in WordPress through which we can fix problems, import and export content, etc. There are two types of tools: built-in WordPress tools and tools provided by plugins, such as the site health management option.
- Available tools: you can see all the current available tools on your wordpress website.
- Import: Import tool helps to bring something to your wordpress website from outside. Such as, importing plugins, themes, media files, web contents, blogs, or importing a fully created website by freelancer to your wordpress account.
- Export: Exporting means sending your posts, pages, media files, to other platforms or websites. Especially, exporting used for sending website files to another wordpress website to import.
Settings: Setting is the core center of a website, you need to set or order your website by utilizing setting options. There are seven setting options below:
- General: general settings options are used for customizing some fundamental aspects of a website. For example,
- Site Title: Site title is a name of your website that appears in a header area of your website and also in search engines.
- Tag line: Tag line is a brief line of what your website is about, giving the audience a clear message or quick hook about your site’s purpose. Often it appears after the site title.
- Site Icon: Site icon is a tiny icon of your website that you have to upload between 512px to 512px which you’ll see in the browser tab, bookmark bars, etc.
- WordPress Address (URL): URL is an address of a web page. Such as, https://jaberhossen.com. And wordpress address is an url or direction where all the core files of a wordpress website will be stored.
- Site Address (URL): Site address is the url link of your website homepage like mine one shown earlier where website visitors find your website with this address. Generally, site address and wordpress address are the same unless you choose a separate directory for each of them to store the files.
- Administration Email Address: It is an email address used for log into your wordpress account and notifications from wordpress related activities such as you post a blog, then you can see the notification of it in this email address. Though, you can change it anytime if necessary.
- Membership: This option is for giving permission to the user registrations. If you don’t want any users to be involved in your wordpress admin area, keep the box unchecked.
- New user default role: A default role for newly assigned users from editor to subscriber. Keep it as a subscriber.
- Site Language: A language that represents your website in your selected language to the audience. Additionally, you can set multiple languages for your website based on location by leveraging plugins.
- Time Zone: Time zone is setting time depending on your location or audience location to post blogs, contents, etc.
- Date Format: There are several types of date format in this section; F J, Y or Y-m-d, etc. I think September 15, 2025 is best.
- Time Format: select the (g: i a) format 4:09 am.
- Week Starts on: Select weekday Monday by default for wordpress website.
- Writing Settings Page: This option introduces some functional aspects of post settings.
- Default Post Category: If you have already categorized your posts into many and you removed one of the blog posts from a specific category, then this post by default will be categorized to your selected default category.
- Default Post Format: Post format is how you want your visitor to see a post in a style standard, chat, quote, aside, etc.
- Post Via email:
- Reading Setting page: Reading setting is about how your reader will find your reading materials on your website. Such as, blog posts reading.
- Your homepage displays: Select the latest posts option, if your website has blogs. Or you can select the static page option for a specific page that will be shown to your visitors as a post page.
- Blog pages show at most: This option is about how many posts you want to show per page of your website. Select any of the digits based on your need.
- Syndications feeds show the most recent: This option is for how many recent posts your visitor can track through wordpress wordpress RSS feed application.
- For each post in a feed, include; if you want your visitors to see an excerpt or summary of your posts in a browser, then select the excerpt option and if not select the full text option.
- Search engine visibility: This option is for discouraging visitors to see your website live by checking the box option. This is beneficial when you customize your website to stop the search engine to show your website temporarily. Though, hostinger has this option in their hostinger plugin.
- Discussion Settings: Discussion setting is for determining interaction between your website and site visitors.
- Default post settings: In this section, check all the three options to allow your post to link internally & externally, and allow the visitor to comment in your new post.
- Other comment settings: if you want more control on the comment section, then you can explore them. Such as, Commentor must fill out the name and email, your wordpress users must be signed up and logged in to leave a comment to your post, selecting a time frame to close comments for old posts; no one will comment after this time frame, enabling threaded or nested comments which means visitors can reply to each others comments, etc.
- Comment pagination: This option is for choosing how many comments you want to showcase in your posts or pages.
- Email me whenever: check these two boxes to get notified whenever someone comments to your post or page for observation and moderation.
- Before a comment appears: if you approve a comment then it will be displayed in your post or page.
- Comment moderation: If you find too many links or suspect anything unusual, then moderation is mandatory.
- Disallowed comment keys: When a comment contains any of these words in its content, author name, URL, email, IP address, or browser’s user agent string, it will be put in the Trash. One word or IP address per line. It will match inside words, so “press” will match “WordPress”
- Avatars: Avatar is a little icon that you will see beside the commenter’s name. You can check the Show Avatar box based on audience ages, or default avatar for who doesn’t have the custom avatar image.
- Media settings: media setting is for determining how your media files will be shown throughout your website content. For example, determining width and height of each type of images like thumbnail size, medium size, large size. This setting is useful when you upload images to your posts and pages.
- Permalink settings: permalink setting is your website URL setting, how your posts and pages link will be depends on your chosen structure from any of the permalink setting options. And the Ideal and best is choosing post name option due to seo factors and simplicity. Furthermore, you can choose custom structure by attaching any of your categories name or tags.
- Privacy settings: This privacy setting option will allow you to add and create a privacy policy page to inform the audience how you collect, use, store, and protect data.